In this article, we'll cover configuring the generic Git connector. This can be used to configure a source control connection to any tool that uses Git as the underlying technology behind their source control repository. These tools include, but are not limited to: GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket, Azure Repos, SourceForge, CodeCommit (AWS). These tools leverage Git’s distributed version control capabilities and often add layers of features like permissions management, visualizations, integrations, and CI/CD pipelines.
The below documentation page will use Azure Repos as the example tool to connect to, however, steps to connect to other tools will be very similar.
First, navigate to Workspace -> Connectors, add a new Git connector.
The configure connector dialogue has three tabs:
Details: Where the connector type and name is set.
Connection: The connection and configuration information for the connector.
Traceability: Shows which Automation Frameworks in the workspace use this Git connector.
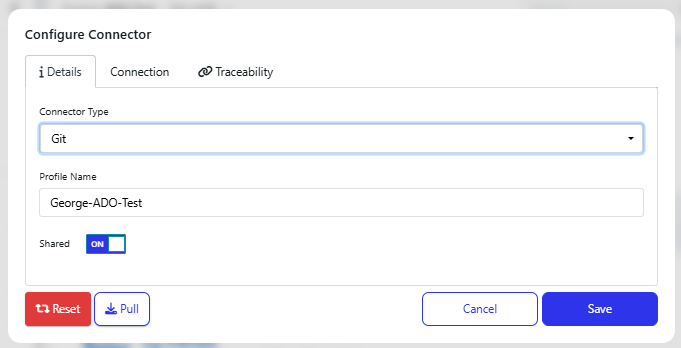
Select Git from the Connector Type dropdown and give this a recognisable Profile Name. Also choose if you would like this connector to be shared among all users in the workspace.
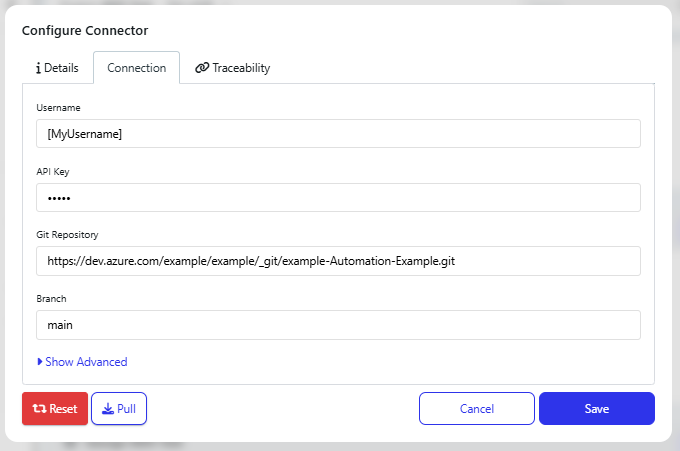
In the connection tab, configure the following information:
Username: The user you would like to commit code with in Git. For pushing code to Azure Repos, you should use the email address you use to login to Azure DevOps.
API Key: In Azure Dev Ops, this is a personal access token - https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/organizations/accounts/use-personal-access-tokens-to-authenticate?view=azure-devops&tabs=Windows - this personal access token must have read and write access to the target repository.
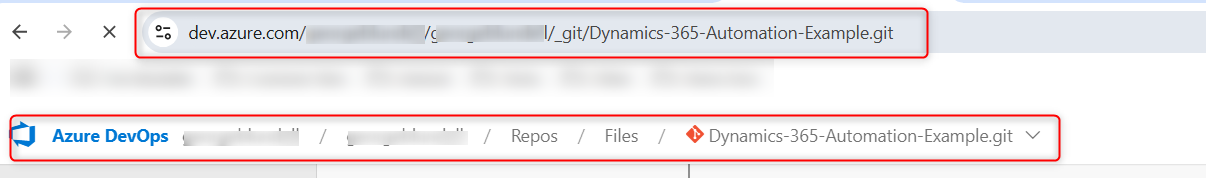
Git Repository: The Git repository URL, you will be able to copy this from either Git locally, or from your repository tooling. Here is the example from Azure DevOps.
Commit Branch: Defines the branch you want to commit code to in Git, this must already exist in Git before committing code from Quality Modeller.
There are a number of Advanced optional fields:
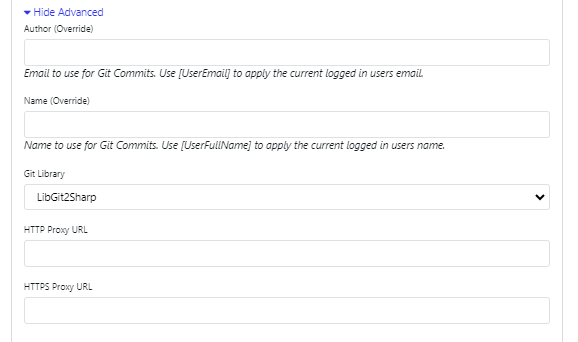
Author (Override): Allows you to override the Author of the code commit. This can be hard coded or you use [UserEmail] to apply the current logged in users email.
Name (Override): Allows you to override the Name associated with a code commit. This can be hard coded or you use [UserFullName] to apply the current logged in users name.
Git Library: This field lets you choose the underlying library that handles Git operations. This can be set to LibGit2Sharp, a C# wrapper around the native Git library, or Native.
HTTP Proxy URL: This field is where you specify the URL of an HTTP proxy server if your network requires it to access external resources over HTTP. For example, http://proxy.mycompany.com:8080. In this example, the proxy server’s URL is
proxy.mycompany.com, and it’s using port8080. The proxy would forward your tool’s HTTP requests to Git.HTTPS Proxy URL: This field is used to specify the URL of an HTTPS proxy, which handles encrypted HTTPS traffic. For example, https://secure-proxy.mycompany.com:443. In this example, the proxy server is
secure-proxy.mycompany.com, and it is listening on port443(the standard port for HTTPS traffic)
Finally, there are a number of User Actions that can be applied to the connector.

Reset: Clears the temporary copy of the Git repository that Quality Modeller stores, this can be useful to run as a troubleshooting step if something goes wrong.
Pull: Pulls the latest version of the Git repository into Quality Modeller.
Cancel: Cancels any changes made to the configurations.
Save: Saves changes.